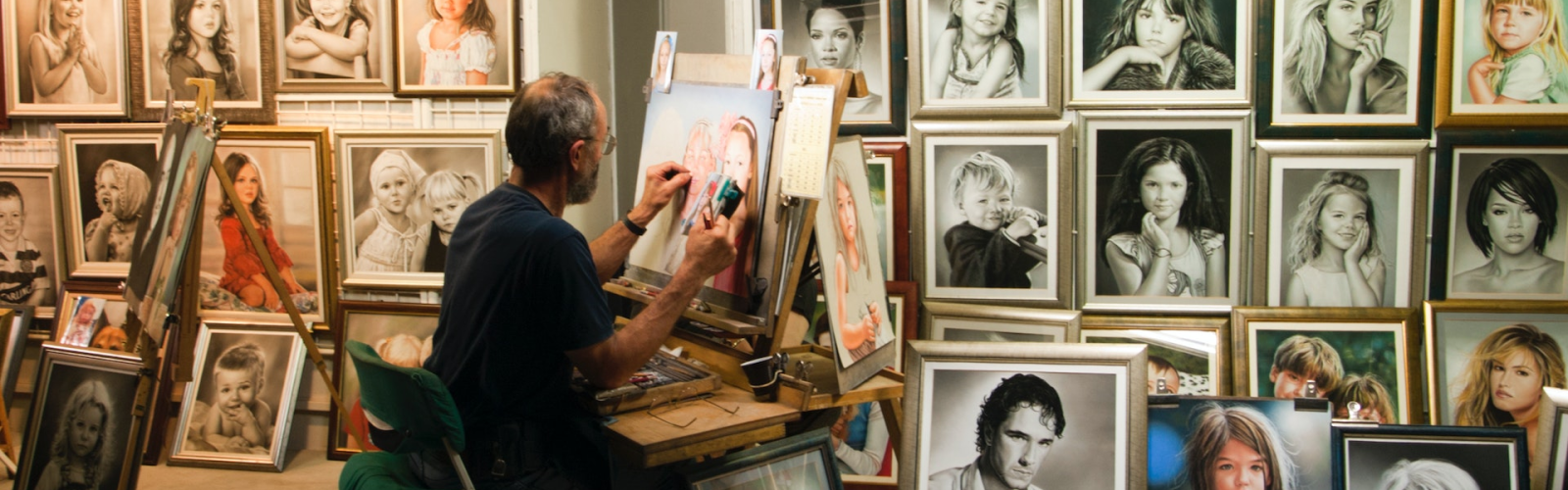
From generating lifelike images to composing symphonies in seconds, digital creativity is undergoing a radical transformation. What was once the exclusive domain of human imagination is now a shared canvas between people and algorithms, where ideas can be sketched, tested, and brought to life faster than ever before. This shift isn’t about replacing human creativity but amplifying it, giving innovators, marketers, designers, and storytellers new ways to experiment, iterate, and build.
The rise of top AI tools has reshaped how we approach creative work, strategy, and collaboration. Instead of staring at a blank page or struggling to visualize abstract concepts, individuals and teams can now co-create with systems that analyze massive amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate fresh possibilities. Used thoughtfully, these technologies can help people go beyond their usual limits, challenge assumptions, and explore ideas they never would have considered alone.
1. Turning Vague Ideas into Concrete Concepts
One of the hardest parts of any creative process is the beginning—when an idea is half-formed and difficult to express. Intelligent generators make it possible to turn a rough thought into something tangible in moments. Writers can outline complex narratives, marketers can shape campaign angles, and product teams can sketch out feature sets. This rapid concepting phase removes the friction of getting started, allowing more time for refinement and originality.
2. Generating Visuals at the Speed of Thought
Visual creativity often requires specialized skills, expensive tools, and long production cycles. Modern systems for image and video generation compress that entire process. Designers can explore different styles, colors, or layouts with quick prompts instead of dozens of manual iterations. Brand builders can preview variations for logos, social content, or landing page graphics in minutes. This visual agility helps teams test bold directions early, then polish the most promising results with human expertise.
3. Supercharging Content Creation Across Formats
Blog posts, scripts, newsletters, ad copy, and product descriptions all compete for time and attention. Automated content engines give creators a starting scaffold for nearly any format. They can suggest structures, generate outlines, and offer alternative phrasings that align with different tones or audiences. Rather than replacing original writing, this workflow lets specialists focus on insight, storytelling, and brand voice—while the system handles the repetitive or formulaic layers beneath.
4. Unlocking Data-Driven Storytelling
Data can be a powerful storytelling tool, but raw numbers rarely inspire. Analytical models can sift through huge datasets, identify trends, and transform those patterns into human-readable narratives. For example, a marketer can quickly discover which audience segments respond to specific messages, then shape compelling stories around those insights. Product teams can surface hidden behavioral patterns to inform new features. The blend of analysis and narrative helps organizations communicate insights in more imaginative and persuasive ways.
5. Personalizing Experiences at Scale
Personalization used to be limited to simple rules like including a first name in an email. Now, advanced systems can dynamically adjust content, visuals, and recommendations based on real-time context and behavior. Whether it’s tailoring learning journeys, customizing product recommendations, or adapting app interfaces, adaptive engines enable experiences that feel uniquely crafted for each user. This level of customization encourages more creative thinking about how brands and platforms interact with individuals, not just segments.
6. Enhancing Collaboration Across Disciplines
Creative work is rarely done in isolation. Yet cross-functional collaboration—between designers, developers, writers, strategists, and stakeholders—can be time-consuming and messy. Shared, intelligent workspaces help teams brainstorm, organize ideas, summarize discussions, and track decisions. Automatic transcription and summarization turn meetings into structured knowledge. Suggestion engines highlight connections between projects or concepts that people might overlook. The result is a more fluid environment where diverse minds can explore possibilities together, supported by a system that keeps everything aligned.
7. Rapid Prototyping for Products and Experiences
Building a new product, service, or digital experience typically requires multiple design and development cycles. Today, teams can prototype user flows, interfaces, copy, and logic far more quickly. Simulations and interactive mockups can be generated and adjusted in hours instead of weeks. This accelerated experimentation invites bolder ideas because the cost of failure drops dramatically. Teams can test unconventional directions, gather feedback early, and refine based on real reactions rather than assumptions.
8. Exploring New Creative Genres and Mediums
As new capabilities emerge, entirely new creative genres are forming. Interactive narratives, immersive branded experiences, dynamic artwork, and adaptive music are just a few examples. Individuals who previously felt locked out of certain fields—such as video production, illustration, or game design—can now participate using intuitive interfaces and automated assistance. This broadening of the creative ecosystem leads to more diverse perspectives and unconventional outputs, expanding what audiences expect and enjoy.
9. Challenging Cognitive Biases and Habits
Human creativity is powerful, but it is also shaped by habits and biases. Systems trained on wide-ranging data can propose ideas that fall outside a person’s usual patterns. When used critically and responsibly, this can act as a creative mirror—surfacing alternative directions, questioning assumptions, and suggesting combinations that feel counterintuitive. Teams can then evaluate these suggestions, draw inspiration, and refine them in line with their goals, values, and audience needs.
10. Making High-Level Strategy More Imaginative
Strategic planning often gets bogged down in spreadsheets and slide decks. Intelligent assistants can simulate scenarios, summarize research, and model potential outcomes under different conditions. This frees leaders to spend more time thinking about bold directions, long-term narratives, and differentiated positioning. Rather than guessing which ideas are viable, they can compare multiple futures, stress-test concepts, and then rally teams around strategies that are both visionary and grounded in data.
Conclusion: Creativity as a Shared Capability
The expanding landscape of intelligent systems is not a threat to human originality; it is a catalyst. By handling routine tasks, surfacing hidden patterns, and making complex production processes accessible, these technologies expand who can create, what they can attempt, and how quickly they can move from concept to reality. The most remarkable breakthroughs are emerging where people treat these systems as collaborators, not just tools—combining human judgment, emotion, and context with algorithmic speed and scale.
As adoption grows, the real advantage will belong to those who ask better questions, design more thoughtful prompts, and build workflows that keep ethics, authenticity, and audience trust at the center. In that environment, technology becomes a partner in exploration, helping individuals and organizations go far beyond incremental improvements and rethink what’s possible in their work, their industries, and their creative lives.